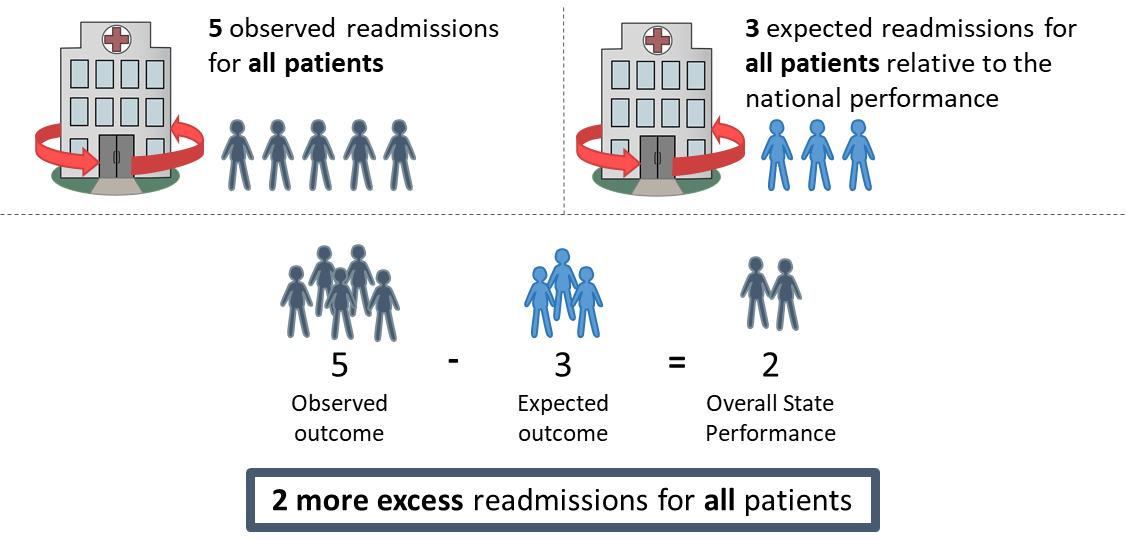
How This Is Calculated
The following hypothetical example demonstrates how the visualization is calculated, using Medicare and Medicaid dual eligibility as the social risk factor:
1. Overall state performance is calculated for the combined dually eligible ("dual") and non-dual population. Per 1000 admissions in the state:
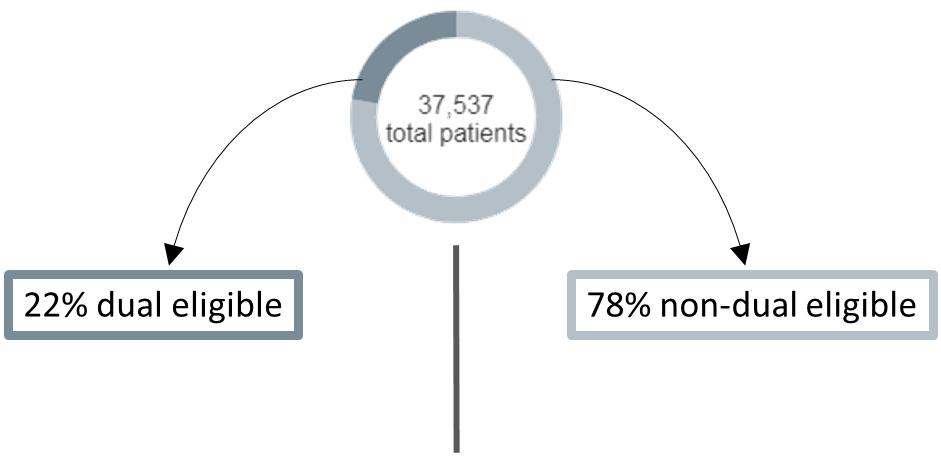
2. Population of dual and non-dual patients is calculated as the percent of each population out of the entire state population.
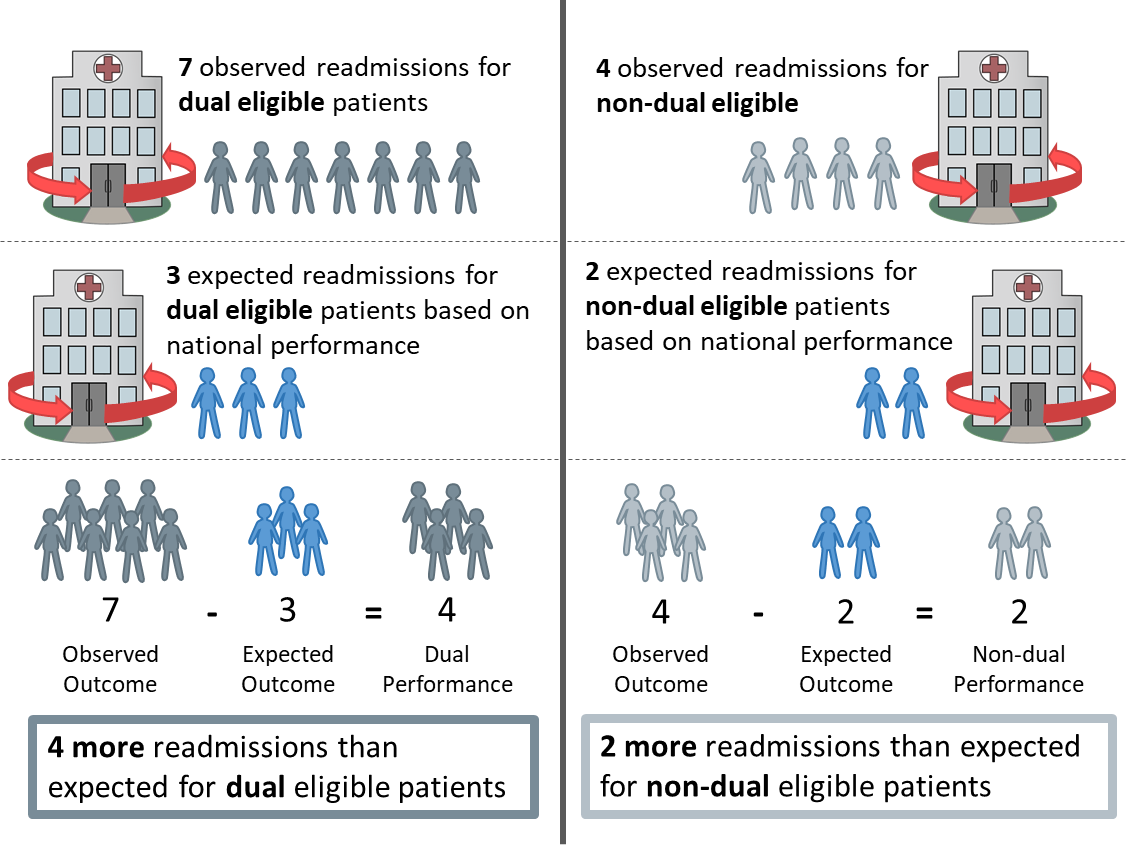
3. Performance is calculated for the dual and non-dual populations for each state by calculating the difference between the observed outcome and the expected outcome based on the national performance for each state. Per 1000 admissions in the state:
4. The disparity between the dual and non-dual population is calculated as the absolute difference between the dual and non-dual performance.
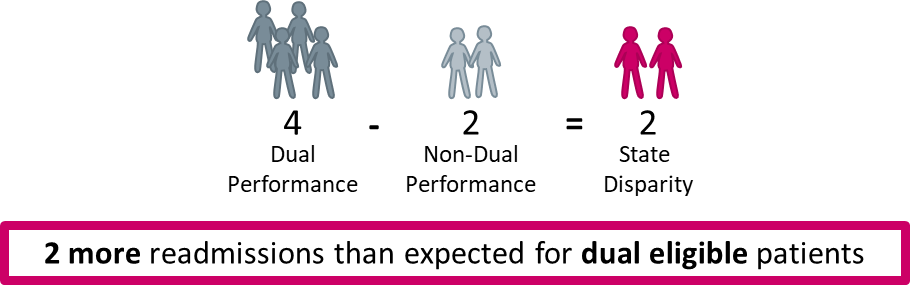
Notes
Beginning with the 2019 reporting year, the stroke readmission measure was removed from this data visualization because this measure is no longer reported in the Inpatient Quality Reporting Program (IQR). This measure’s results are still available in reporting years prior to 2019.
Table 1. Social Risk Factors Definitions
|
Social Risk Factor |
Definition |
|---|---|
| Dual Eligibility Status | Patients are in this category if they are a part of Medicare Part A or Medicare Part B as well as Medicaid. |
| Poverty Line | Patients who fit into this category have a family income that is lower than 90 percent of people in the US. |
| Low Education | Patients fit into this category if they have a level of education lower than 90 percent of people in the US. |
| Unemployed | Patients from zip codes where more than 11.5% of the residents aged 16 years or older are in the labor force who are unemployed and actively seeking work. |
| AHRQ SES Index Score | Patients from zip codes with an Agency for Healthcare Research & Quality (AHRQ) socioeconomic status (SES) index score below 31.8. |
Methodology Sources
AMI, COPD, Heart Failure, and Pneumonia Readmission Measures Methodology: DeBuhr J, McDowell K, Grady J, et al. 2020 Condition-Specific Measures Updates and Specifications Report Hospital-Level 30-Day Risk-Standardized Readmission Measures: Acute Myocardial Infarction – Version 13.0, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease – Version 9.0, Heart Failure – Version 13.0, Pneumonia – Version 13.0. https://qualitynet.cms.gov/files/609524402be51c001edf6195?filename=2020_Readmission_Meas_Updates_Specs.zip. Available as of Spring 2020.
CABG and Hip/Knee Arthroplasty Readmission Measures Methodology: DeBuhr J, McDowell K, Grady J, et al. 2020 Procedure-Specific Measures Updates and Specifications Report Hospital-Level 30-Day Risk-Standardized Readmission Measures: Isolated Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) Surgery – Version 7.0, Elective Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA) and/or Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) – Version 9.0. https://qualitynet.cms.gov/files/609524402be51c001edf6195?filename=2020_Readmission_Meas_Updates_Specs.zip. Available as of Spring 2020.
AMI, COPD, Heart Failure, Pneumonia, and Stroke Mortality Measures Methodology: DeBuhr J, McDowell K, Grady J, et al. 2020 Condition-Specific Measures Updates and Specifications Report Hospital-Level 30-Day Risk-Standardized Mortality Measures: Acute Myocardial Infarction – Version 14.0, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease – Version 9.0, Heart Failure – Version 14.0, Pneumonia – Version 14.0, Stroke – Version 9.0. https://qualitynet.cms.gov/files/607333022402a2001eb9e25d?filename=2020_Mort_Meas_UpdtsSpecsResrc.zip. Available as of Spring 2020.
CABG Mortality Measure Methodology: DeBuhr J, McDowell K, Grady J, et al. 2020 Procedure-Specific Measure Updates and Specifications Report Hospital-Level 30-Day Risk-Standardized Mortality Measure: Isolated Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) Surgery – Version 7.0. https://qualitynet.cms.gov/files/607333022402a2001eb9e25d?filename=2020_Mort_Meas_UpdtsSpecsResrc.zip. Available as of Spring 2020.
Hip/Knee Arthroplasty Complication Measure Methodology: DeBuhr J, McDowell K, Grady J, et al. 2020 Procedure-Specific Measure Updates and Specifications Report Hospital-Level Risk-Standardized Complication Measure: Elective Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA) and/or Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) – Version 9.0. https://qualitynet.cms.gov/files/60734125aba8620022335c08?filename=2020_THA_TKA%20Comp_MUS_Rpt.zip. Available as of Spring 2020.
AMI, Heart Failure, Pneumonia, and Elective Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA) and/or Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) Payment Measures Methodology: DeBuhr J, McDowell K, Grady J, et al. 2020 Measure Updates and Specifications Report Hospital-Level Risk-Standardized Payment Measures: Acute Myocardial Infarction – Version 9.0, Heart Failure – Version 7.0, Pneumonia – Version 7.0, Elective Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA) and/or Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) – Version 6.0. https://qualitynet.cms.gov/files/6092dd81fd340b002259fde6?filename=2020_Payment_AUS_Rprt.zip. Available as of Spring 2020.
AMI, Heart Failure, Pneumonia Excess Days in Acute Care Measure Methodology: DeBuhr J, McDowell K, Grady J, et al. 2020 Condition-Specific Measures Updates and Specification Report Hospital-Level 30-Day Risk-Standardized Excess Days in Acute Care Measures: Acute Myocardial Infarction – Version 5.0, Heart Failure – Version 5.0, Pneumonia – Version 4.0. https://qualitynet.cms.gov/files/6092b1cdfd340b002259fdaf?filename=2020_EDAC_MeasMethRpt.pdf. Available as of Spring 2020.
Hospital-Wide Readmission Measure Methodology: DeBuhr J, McDowell K, Grady J, et al. 2020 All-Cause Hospital-Wide Measure Updates and Specifications Report: Hospital-Level 30-Day Risk-Standardized Readmission Measure – Version 9.0 https://qualitynet.cms.gov/files/609524402be51c001edf6195?filename=2020_Readmission_Meas_Updates_Specs.zip. Available as of Spring 2020.